Fe Cation Charge

Negative charge. Does not retain Attracts and retains cations. Figure 1: Substitution of silica by aluminum in soil clay particles causes clays to have a negative charge. Because of this negative charge, the soil can hold on to positively charged cations such as calcium (Ca 2+), magnesium (Mg ) and potassium (K+). The Fe has to cancel out the charge of the -2. You then have to look at your periodic table and see if one of iron's oxidation states is a +2. The iron is the cation and the hydroxide ion is the anion. Cr(OH)3-Same as the FE(NO3)2, the polyatomic OH is hydroxide. It has a charge of -1, there are three of them so all together is it a charge of -3. I know that the charge of the Fe cation is 3+, but is this the correct way so find the charge of Fe? O's charge is always 2- & 2- 'times' (O)3 = -6 because the charge of an ionic compound is. Cations & Anions Cations include everything from hydrogen, with a +1 positive charge, to aluminum, with a +3 positive charge. Anions include phosphate, nitrate, and other essential elements that hold a -1 or -2 charge. Table 1 shows the most common cations and anions along with their chemical formula and charge. Give either the name or formula (with the correct charge) for each of the cations.

Department of Chemistry and Physics |
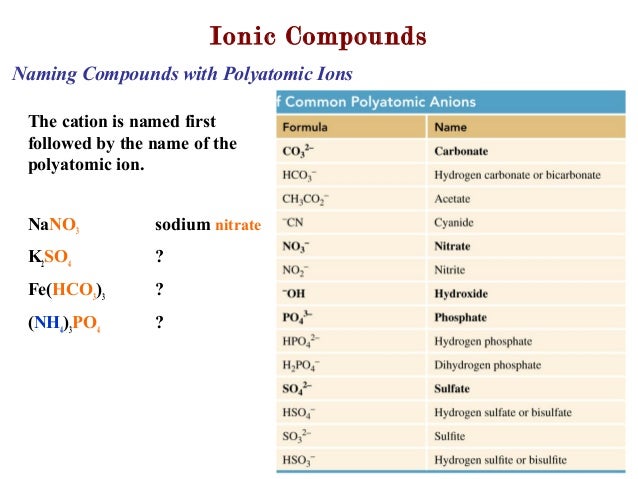
| Answers |

Sulfur Ion Charge
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula |
| zinc | Zn+2 | chromium(II) | Cr+2 |
| mercury(II) | Hg+2 | hydronium | H3O+ |
| ferric | Fe+3 | manganese(II) | Mn+2 |
| hydrogen | H+ | strontium | Sr+2 |
| silver | Ag+ | nitronium | NO2+ |
| barium | Ba+2 | stannic | Sn+4 |
| magnesium | Mg+2 | mercuric | Hg+2 |
| chromic | Cr+3 | iron(III) | Fe+3 |
| copper(I) | Cu+ | calcium | Ca+2 |
| sodium | Na+ | lead(II) | Pb+2 |
| calcium | Ca+2 | manganese(III) | Mn+3 |
| tin(II) | Sn+2 | ammonium | NH4+ |
| nitronium | NO2+ | potassium | K+ |
| manganous | Mn+2 | hydronium | H3O+ |
| chromium(III) | Cr+3 | tin(IV) | Sn+4 |
| mercury(I) | Hg2+2 | ferrous | Fe+2 |
| strontium | Sr+2 | copper(II) | Cu+2 |
| copper(I) | Cu+ | chromous | Cr+2 |
| manganic | Mn+3 | lithium | Li+ |
| magnesium | Mg+2 | mercury(I) | Hg2+2 |
| stannous | Sn+2 | manganese(III) | Mn+3 |
| cuprous | Cu+ | iron(II) | Fe+2 |
| iron(III) | Fe+3 | barium | Ba+2 |
| hydrogen | H+ | chromium(II) | Cr+2 |
| potassium | K+ | iron(II) | Fe+2 |
| lead(II) | Pb+2 | mercury(II) | Hg+2 |
| lithium | Li+ | cupric | Cu+2 |
| manganese(II) | Mn+2 | mercurous | Hg2+2 |
| ammonium | NH4+ | tin(IV) | Sn+4 |
| sodium | Na+ | chromium(III) | Cr+3 |
| silver | Ag+ | zinc | Zn+2 |
| tin(II) | Sn+2 | copper(II) | Cu+2 |
Carbon Ion Charge
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula |
| hypobromite | OBr- | phosphate | PO43- |
| fluoride | F- | formate | HCOO- |
| acetate | CH3COO- | carbonate | CO32- |
| bromide | Br- | nitrite | NO2- |
| bromate | BrO3- | amide | NH2- |
| formate | HCOO- | sulfate | SO42- |
| dichromate | Cr2O72- | hydride | H- |
| chloride | Cl- | iodate | IO3- |
| oxalate | C2O42- | nitrate | NO3- |
| chlorate | ClO3- | hydrogen carbonate | HCO3- |
| arsenate | AsO43- | chromate | CrO42- |
| sulfite | SO32- | phosphate | PO43- |
| peroxide | O22- | thiocyanate | SCN- |
| arsenite | AsO33- | permanganate | MnO4- |
| cyanate | OCN- | hydrogen sulfate | HSO4- |
| cyanide | CN- | chromate | CrO42- |
| hydride | H- | dihydrogen phosphate | H2PO4- |
| nitride | N3- | chloride | Cl- |
| sulfate | SO42- | nitrate | NO3- |
| hydrogen sulfate | HSO4- | arsenite | AsO33- |
| thiosulfate | S2O32- | fluoride | F- |
| sulfite | SO32- | bromide | Br- |
| hydroxide | OH- | iodide | I- |
| thiocyanate | SCN- | iodate | IO3- |
| permanganate | MnO4- | sulfide | S2- |
| chlorite | ClO2- | oxide | O2- |
| hypochlorite | OCl- | hypobromite | OBr- |
| nitride | N3- | hydrogen phosphate | HPO42- |
| carbonate | CO32- | chlorite | ClO2- |
| hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate | HCO3- | dichromate | Cr2O72- |
| oxalate | C2O42- | bromate | BrO3- |
| nitrite | NO2- | sulfide | S2- |
| acetate | CH3COO- | perchlorate | ClO4- |
| hydrogen phosphate | HPO42- | arsenate | AsO43- |
| oxide | O2- | iodide | I- |
| cyanide | CN- | amide | NH2- |
| cyanate | OCN- | peroxide | O22- |
| chlorate | ClO3- | dihydrogen phosphate | H2PO4- |
| thiosulfate | S2O32- | hypochlorite | OCl- |
| hydroxide | OH- | perchlorate | ClO4- |